-
For many of us, the idea of having such a chip implanted in our body is an appalling one, but a 2021 survey of more than 4,000 people across the UK and the European Union found that 51% would consider it.
However, without giving a percentage figure, the report added that "invasiveness and security issues remained a major concern" for respondents.
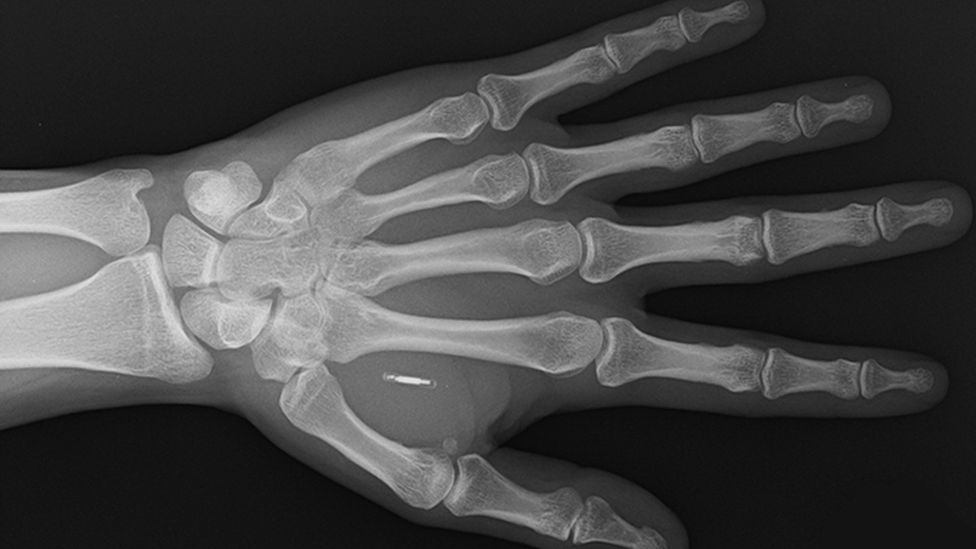
The technology Walletmor uses is near-field communication or NFC, the contactless payment system in smartphones. Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards.
Mr Paumen says he doesn't have any of these worries.
"Chip implants contain the same kind of technology that people use on a daily basis," he says, "From key fobs to unlock doors, public transit cards like the London Oyster card, or bank cards with contactless payment function.
"The reading distance is limited by the small antenna coil inside the implant. The implant needs to be within the electromagnetic field of a compatible RFID [or NFC] reader. Only when there is a magnetic coupling between the reader and the transponder can the implant can be read."
He adds that he is not concerned that his whereabouts could be tracked.
"RFID chips are used in pets to identify them when they're lost," he says. "But it's not possible to locate them using an RFID chip implant - the missing pet needs to be found physically. Then the entire body gets scanned until the RFID chip implant is found and read."
Yet the issue with such chips, (and what causes concern), is whether in the future they become ever more advanced, and packed full of a person's private data. And, in turn, whether this information is secure, and if a person could indeed be tracked.



0 Comments